The world's largest WSE-2 processor is released!
2021-04-23
I don’t know if you still remember the A100 GPU released by NVIDIA last year. As another big computing card three years after the launch of the V100, its performance is 20 times higher than that of the V100. NVIDIA calls it the largest 7nm chip with an area of 826 mm2. The start-up company Cerebras recently released the second-generation Wafer Scale Engine (WSE-2) chip, which won the throne of the largest chip under 7nm.
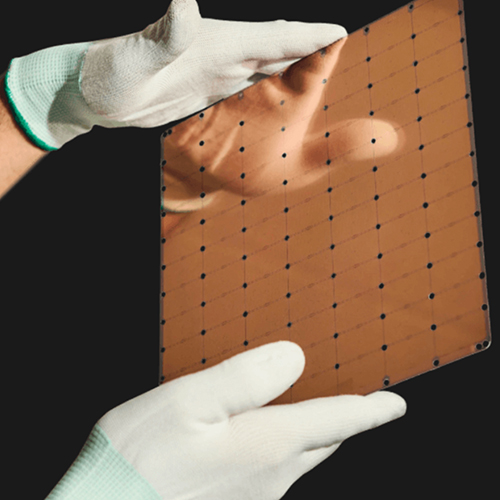
WSE-2 chip/ Cerebras
From 2015 to 2020, the world's calculations on training large models have reached 300,000 times. The limitation of AI is more like the limitation of computing power, not just application and creativity. It may take weeks or even months to verify a conjecture and train a new model. Cerebras' WSE-2 aims to solve these problems that affect the speed of innovation.
One wafer = one chip
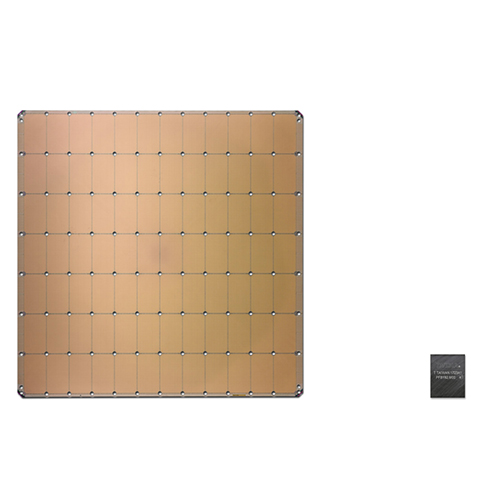
Area size comparison between WSE-2 and A100 / Cerebras
WSE-2 was replaced from the previous generation of 16nm process to 7nm. Although the area remains the same, the density advantage of the new process doubles the number of transistors to 2.600 billion, and the number of AI cores has increased to 850,000. Cerebras is a direct benchmark against Nvidia's A100 in terms of parameter introduction. Compared with the A100 of 826 mm2, the WSE-2 of 46225 mm2 is 56 times that of the former. The on-chip memory of WSE-2 is 40GB, which is a thousand times that of A100, and the memory bandwidth is tens of thousands of times that of A100. WSE contains 850,000 sparse linear algebra computing (SLAC) cores optimized for AI applications, which is very suitable for neural network operations.
Cerebras also pointed out that memory is also an important part of computing. Take the A100 mentioned above. The A100 has only 40MB of L2 cache, but 40GB of HBM2 memory, but the disadvantage of this graphics processor is that this kind of graphics memory is often off-chip memory, and the speed is too slow, and the delay is too long. high. The 40GB memory of WSE-2 is evenly distributed on the AI core, and the bandwidth can reach 20PB/s.
In fact, as early as last year's Hot Chips conference, Cerebras had revealed this new processor with 850,000 AI cores, but due to some delays, they could not release it in time last year. Cerebras co-founder Andrew Feldman mentioned in a recent interview that after working with customers for a year, they have learned some lessons and integrated them into the new AI core, so this delay is likely due to Improvement of AI core micro-architecture.
In the past, a wafer had to be cut into multiple chips, packaged and then sold as a processor. Cerebras's solution is wafer-level integration technology, which directly uses the largest area of a wafer to produce a single chip. However, considering that rectangular chips are still the most efficient choice at present, it is naturally impossible to directly manufacture the entire circular wafer. For the chip, Cerebras also selected the largest square from a wafer. Although from the area of a 12-inch wafer, only 2/3 of the area is used to manufacture a WSE-2, compared with the price of the chip, even if these leftovers are wasted, the loss is only a drop in the ocean. To know that Cerebras sold two WSE-1 based systems to the Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center, but made a profit of nearly $5 million.
AI computing platform based on WSE-2
But putting a more powerful chip in an old system may not necessarily achieve full performance, but may highlight the bottleneck of the original system, such as communication structure, chip I/O, power supply, and heat dissipation. It's like putting a Ferrari engine in a Volkswagen, and it can't run faster than the former.
CS-2 cooling system / Cerebras
Based on WSE-2, Cerebras' systems and software platforms, Cerebras has also launched a new generation of deep learning system CS-2 to break through system limitations. Such a powerful performance naturally requires a powerful power supply. CS-2 uses a 9+3 redundant power supply configuration to drive WSE-2. However, this kind of power supply naturally faces the challenge of heat dissipation. Cerebras uses a water-cooled heat dissipation system inside the CS-2 to dissipate heat from the WSE-2, and then air-cooled to lower the water temperature. At the same time, the space occupied by the CS-2 is not large. This 26-inch high machine only occupies 15U of rack space. Although it is larger than Nvidia's HGX A100 system, this space occupation is still acceptable considering the performance improvement. of.

CS-2 System/ Cerebras
According to Cerebras, both WSE-2 and CS-2 will be launched in the third quarter of this year, and the price of CS-2 will rise from CS-1’s 2 to 3 million US dollars to "several million" US dollars. digital.
summary
Although Cerebras' WSE-2 is a performance monster, its application is not as wide as the A100, and it is more like a niche market. Take some customers of WSE-1, most of them are doing some biological and medical research, such as cancer treatment, drug discovery, etc., and they are mostly used in supercomputing centers and national laboratories, such as the Pittsburgh Supercomputing Center mentioned above. And Argonne National Laboratory. Nvidia’s A100 can be used for various AI and HPC applications. This is also something that Cerebras’ current solutions have not broken through. However, considering Cerebras’ positioning is not to achieve comprehensive coverage, focusing on one market is what Cerebras can do. The reason for being so good.
In fact, the most worthwhile breakthrough is this wafer-level integration technology. Although chip designers hope to obtain more chips from a single wafer and obtain higher profits, this kind of purely performance-oriented chips is suitable for today. Many Power-hungry applications. Having said that, achieving the yield of this type of chip is also a big challenge, and not every company achieves 100% yield on WSE-2 like Cerebras.